分子医薬学(協力)トキシコゲノミクス
研究室概要
トキシコゲノミクス研究室という名前は、聞き慣れないことと思います。名古屋大学大学院医学系研究科は、平成25年度より「総合医学専攻」という単一専攻に組織改革を行い、これに伴って基礎医学と臨床医学の領域に、新たに「統合医薬学領域」が加わり、三領域体制になりました。この統合医薬学領域は創薬を主たるkey wordとして研究と教育を充実させ、優れた人材の輩出と研究成果を期待されています。こうした背景から、「トキシコゲノミクス」研究室、和訳をしますと「毒性遺伝子学」、という名称の『医薬品の安全性科学』を専門とする研究室が新たにスタートしました。
日常的に処方される薬による症状改善の程度は個人によって著しく異なり、疾病によっては半分以上の患者様に薬効が認められない場合もめずらしくありません。全体の約10%のヒトに何らかの副作用が発現しているという米国FDA(Food and Drug Administration)の統計もあります。1992年の米国の統計では、薬に起因する死亡が死因の4番目であると報告され、薬の副作用による社会的損失は膨大なものであり、その頃から、薬の安全性を確保する研究の必要性が強く認識されるようになりました。薬の副作用や毒性において、その予測や回避が難しい場合において、そのほとんどのケースは、薬の薬理や薬効に全く関係なく発現します。副作用の発現を説明するには、薬が全身でどのように移動し、解毒されるか、また薬の構造変換と毒性の関わりを理解する必要があります。すなわち、「薬物動態」分野の研究領域になります。
近年の薬物動態分野の研究の顕著な発展に伴って、創薬段階における臨床試験での開発中止が、薬物動態に起因するケースは、1991年、2000年、2011年で、40%、9%、1%へと激減してきています。しかし、副作用・毒性発現に起因する開発中止のケースは、13%、20%、19%と高水準のままであり、とりわけ、市販後に予期せぬ副作用の発現によって撤退・発売停止のケースも含めて、その原因は薬物性肝障害の発症が最も多いことが知られています。よって、厚生労働省のみならず、FDAやEUにおいても、予測が難しい薬物性肝障害の解明研究が特別推進課題と位置づけられています。
近年、医薬品の安全性を確保するための、薬物動態及び薬物代謝の研究には、ゲノムのみならず、メッセンジャーRNA、蛋白質、マイクロRNAの広汎な理解に加え、リン酸化や脱アセチル化等の因子や食事や生活のストレスの影響等の理解も必要であることが明らかにされつつあり、極めて幅広い研究が必要になっています。こうした背景から、横井毅は金沢大学大学院薬学系の教授として16年間、薬物代謝と毒性の研究を行ってきました。その経験をさらに発展させ、「トキシコゲノミクス」研究室では、薬による副作用の研究を中心に、主に薬物性肝障害の基礎および臨床研究を充実させて行きたいと考えています。特に免疫学的因子と、極めて初期に応答するマイクロRNAを考慮した、肝障害発症機序の包括的理解と、その予測試験系の構築を目指します。さらに、安全性に関わる基礎的研究のみならず、臨床での様々な薬に関連する問題を解決する研究課題を設定し、薬を通して直接臨床に資する研究を目指したいと考えています。加えて、他機関との共同研究、臨床共同研究のみならず、製薬会社、CRO、規制当局も集う、情報交換と情報発信の場の形成を目指し、その為には、研究内容の重要性や社会性を広く発信し、多くの研究員や学生がインタラクションする研究環境を創設したいと考えています。
研究プロジェクト
- 薬物性副作用の動物モデルの作出と発症メカニズムの解明研究
- 薬物性肝障害を予測するin vitro試験系の開発研究
- アシルグルクロナイドの毒性についての研究
- Non-coding RNAが薬物動態・毒性発現に及ぼす影響の研究
- 薬の副作用バイオマーカーとしてのnon-coding RNAの研究
- 薬による重篤な皮膚障害を発症のメカニズムの解明研究
1. 薬による副作用発現の背景
医薬品の開発や安全な臨床使用を妨げる最大の課題は、予測が困難な毒性・副作用 の発現にあると言っても過言ではありません。薬を投与されたヒトの約10%に何らかの副作用が発現しているというFDAの統計もあります。さらに、薬の副 作用に起因する死亡が死因の4番目であるという米国の統計も出され、その社会的損失は膨大であり、薬の安全性を確保する研究の必要性が強く認識されていま す。創薬は定めた薬効標的に対する効果の評価により進められ、細胞系や実験動物を用いて研究されますが、薬の副作用や毒性は、薬理や薬効に関係なく発現する場合が多く、薬物代謝動態に依存していることが知られています。しかし、様々な薬物動態関連因子には、大きな種差と個人差が存在し、これらに起因する毒 性・副作用発現により、優れた候補化合物であって臨床試験が中断される場合が少なくありません。これはヒトにおける毒性・副作用発現を予測するための適切 な試験系が確立していないために生じます。こうした問題を科学的に解決し、社会に資する研究の推進が期待されています。
2. 薬の解毒と副作用発現反応
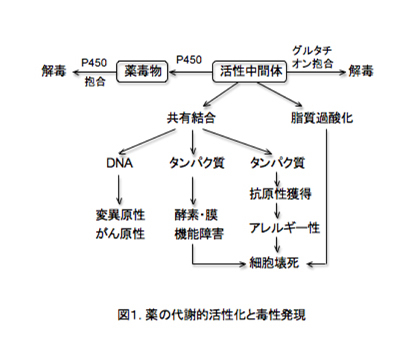
ヒトは高い解毒能を有しており、薬は異物として速やかに解毒されます。一般に、投与された薬の約10%が薬効を発揮するために使われ、残りは速やかに解 毒排泄されます。肝臓は薬を解毒する主要な臓器であり、薬物代謝酵素、特にシトクロムP450が中心となって薬を解毒します。しかし、P450などの代謝 酵素は、解毒と同時に「代謝的活性化」と謂われる反応により、毒性代謝物(反応性中間体)に変換する反応も触媒する場合が少なくありません。その為に薬の 副作用や毒性は主に肝臓に発現しやすく、さらに、問題となる重篤な肝毒性発現は、その頻度が数千から1万例に1件と頻度が極めて低いために、市販後に初めて検出される場合が多く、患者保護と企業経営上の問題を大きくしています。P450による代謝的活性化反応によって生成された「反応性中間体」は、図1にありますように核酸や細胞構成蛋白質などに強く結合し、遺伝毒性、細胞機能障害、臓器障害、アレルギーなど極めて多様な毒性を発現します。
3. 薬の副作用の軽減・回避・予測手法
近年の薬物代謝動態分野の研究の顕著な発展に伴って、臨床試験での 開発中止が、薬物動態に起因するケースは、1991から2011年で、40%から1%へと激減しました。しかし、副作用・毒性発現に起因する開発中止ケー スは、継続的に約20%と高水準のままです。これには、薬の毒性発現には代謝動態関連因子が深く関わっており、その知識が活かされていないことが原因であると考えられます。そこで、私共の研究室では、実験動物とヒトとの「種差」と、ヒトの大きな「個人差」を科学し、克服する研究を目指しています。その為に は、実験動物のin vivoでの肝障害モデルを確立すること、実験動物由来細胞およびヒト由来細胞のin vitro試験系を構築してデータを蓄積し、さらに、毒性の新規発現機序について分子生物学的手法などを用いて検証し、最終的にはヒトin vivoを予測することを目指します。
代表的な研究手法としては、(1) 市販で入手可能であるヒト肝臓組織やヒトヘパトサイトおよび実験動物やそのヘパトサイトを駆使して、被験薬の代謝と毒性を検討します。(2) 代謝物を分析し、構造を明らかにし、さらに代謝酵素を明らかにします。(3) 代謝酵素のリコンビナント発現系を作成して、それらを用いて定量的に反応を検討し、種差と個人差を説明することが可能になります。しかしながら、このよう な手法によって毒性回避手段を提案できる場合は稀であり、極めて複雑な機構が関与している為に、依然として多くの薬において、様々な特異体質性 (idiosyncratic)と謂われる未解明の副作用事例が多く報告され続けています。
4. 免疫炎症因子と薬物性肝障害
私共は薬物性肝障害の発症予測のヒトへの予測性が悪い原因として、 免疫学的な因子の関与を明らかにしてきましたので紹介させて頂きます。ヒトにおける肝障害発症が知られている臨床使用薬について、野生型マウスへの薬の投 与法を工夫して、肝障害モデルを作製することにより研究を進め、ハロタンにはTh17細胞が関与することを明らかにしました。その後、ジクロキサシリン、 フルタミドやメチマゾールによる肝障害発症にはTh2細胞が主に関与していることを報告しました。さらに、α-ナフチルイソチオシアネート、ジクロフェナ クやフルクロキサシリンによる肝障害にはTh17細胞が関与することを明らかにしました。こうした検討結果は、いずれも単回経口投与による急性毒性モデル であり、臨床での一般的な連投による稀な肝障害の発症とは異なると考えられますが、発症機序の予測の研究手段を提供で、ヒトin vitroのスルリーニング系の構築に役立っています。
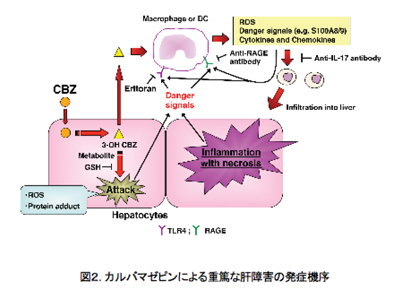
鎮痙薬であるカルバマゼピン (CBZ) は、稀に肝障害を惹起し、アレルギー症状が伴う臨床報告もあります。私共はCBZを野生型マウスに連続経口投与する方法を工夫して、重篤な肝障害発症モデ ルを確立しました。CBZと4種類の主たる代謝物のマウス血中濃度は、1.5-3時間で最大を示し、CYP阻害薬であるトロレアンドマイシンを併用投与す ると肝障害が増悪し、その時の血中濃度の測定から、3位水酸化CBZの関与が強く示唆されました。発症機構を解析した結果、RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation endproduct) や低分子カルシウム結合性蛋白質であるS100A8およびS100A9を介したTLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) の関与が考えられ、各種抗体を用いた肝障害マウスin vivoにおける中和反応は、肝障害を充分に抑制しました。さらに、炎症性サイトカインやケモカインの関与として、Th17細胞が肝障害の増悪に主たる役 割を担っていることを明らかにしました (図2)。このような肝障害モデルマウスの作製と発症機序解明は、臨床における特異体質性薬物性肝障害の回避に繋がる情報を提供できると考えられます。さらに、免疫炎症因子を考慮した、細胞スクリーニング系の立ち上げを行い、類似化合物への適用を提案することができました。
以上、薬物性肝障害を中心に研究内容の一部を紹介しましたが、薬物性の腎臓や血液障害および重篤な皮膚障害などの研究にも取り組んでいます。さらに、non -coding RNAに注目をして、薬物代謝酵素の機能との関わりのメカニズム解明の研究も行っています。今後、薬による副作用の基礎研究を発展させ、臨床に資する研究成果を目指しています。
研究実績
- 2018年
- Matsubara A, Oda S, Akai S, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. Establishment of a drug-induced rhabdomyolysis mouse model by co-administration of ciprofloxacin and atorvastatin. Toxiclol Lett, 2018; 291: 184-193.
- Xu J, Oda S, Yokoi T. Cell-based assay using glutathione-depleted HepaRG and HepG2 human liver cells for predicting drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol In Vitro, 2018; 48: 286-301.
- Oda S, Takeuchi M, Akai S, Shirai Y, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. MicroRNA in rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and hepatocytes and application to circulating biomarkers that discern pathogenesis of liver injuries. Am J Pathol, 2018; 188: 916-928.
- Yamashita S, Oda S, Endo H, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. Neutrophil depletion protects against zomepirac-induced acute kidney injury in mice. Chem Biol Interact, 2018; 279: 102-110.
- Nakajima A, Sato H, Oda S, Yokoi T. Fluoroquinolones and propionic acid derivatives induce inflammatory responses in vitro. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2018; 34: 65-77.
- Sasaki E, Yokoi T. Role of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism and involvement of reactive metabolite formations on antiepileptic drug-induced liver injuries. J Toxicol Sci, 2018; 43: 75-87.
- 2017年
- Yamaura Y, Tatsumi N, Takagi S, Tokumitsu S, Fukami T, Tajiri K, Minemura M, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Serum microRNA profiles in patients with chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or drug-induced liver injury. Clin Biochem, 2017; 50: 1034-1039.
- Oda S, Kato Y, Hatakeyama M, Iwamura A, Fukami T, Kume T, Tsuyoshi Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Evaluation of expression and glycosylation status of UGT1A10 in Supersomes and intestinal epithelial cells with a novel specific UGT1A10 monoclonal antibody. Drug Metab Dispos, 2017; 45: 1027-1034.
- Sho Akai, Shingo Oda, and Tsuyoshi Yokoi. Establishment of a novel mouse model for pioglitazone-induced skeletal muscle injury. Toxicology, 2017; 382: 1-9.
- Shirai Y, Oda S, Makino S, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. Establishment of a mouse model of enalapril-induced liver injury and investigation of the pathogenesis. Lab Invest, 2017; 97: 833-842.
- Oda S, Shirai Y, Akai S, Nakajima A, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. Toxicological role of an acyl glucuronide metabolite in diclofenac-induced acute liver injury in mice. J Appl Toxicol, 2017; 37: 545-553.
- Tomida T, Okamura H, Yokoi T, Konno Y. A modified multiparametric assay using HepaRG cells for predicting the degree of drug-induced liver injury risk. J Appl Toxicol, 2017; 37: 382-390.
- 横井 毅、織田進吾. 薬物代謝・薬物動態研究の最近の動向と展望 -医薬品開発研究を中心として-。化学と生物, 2017; 55: 412-420.
- Iwamura A, Nakajima M, Oda S, Yokoi T. Toxicological potential of acyl glucuronides and its assessment. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2017; 32: 2-11.
- 横井 毅. 薬剤性肝胆膵障害「図解 薬害副作用学 改訂2版」川西正祐、小野秀樹、賀川義之編、南山堂、2017; 282-291.
- 2016年
- Uematsu Y, Akai S, Tochitani T, Oda S, Yamada T, Yokoi T. MicroRNA-mediated Th2 bias in methimazole-induced acute liver injury in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2016; 307: 1-9.
- Iwamura A, Watanabe K, Akai S, Nishinosono T, Tsuneyama K, Oda S, Kume T, Yokoi T. Zomepirac acyl glucuronide is responsible for zomepirac-induced acute kidney injury in mice. Drug Metab Dispos, 2016; 44: 888-896.
- Chiangsom A, Lawanprasert S, Oda S, Kulthong K, Luechapudiporn R, Yokoi T, Maniratanachote R. Inhibitory and inductive effects of Phikud Navakot extract on human cytochrome P450. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2016; 31: 210-217.
- Oda S, Matsuo K, Nakajima A, Yokoi T. A novel cell-based assay for the evaluation of immune- and inflammatory-related gene expression as biomarkers for the risk assessment of drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett, 2016; 241: 60-70.
- Nakajima A, Oda S, Yokoi T. Allopurinol induces innate immune responses through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in HL-60 cells. J Appl Toxicol, 2016; 36: 1120-1128.
- Sasaki E, Iida A, Oda S, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Pathogenetic analyses of carbamazepine-induced liver injury in F344 rats focused on immune- and inflammation-related factors. Exp Toxicol Pathol, 2016; 68: 27-38.
- Akai S, Uematsu Y, Tsuneyama K, Oda S, Yokoi T. Kupffer cell-mediated exacerbation of methimazole-induced acute liver injury in rats. J Appl Toxicol, 2016; 36: 702-715.
- Takai S, Oda S, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Establishment of a mouse model for amiodarone-induced liver injury and analyses of its hepatotoxic mechanism. J Appl Toxicol, 2016; 36: 35-47.
- Fujiwara R, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Structure and protein-protein interactions of human UDP-glucuronosyltansferases. Front Pharmacol, 2016; 7: 388.
- 織田進吾, 横井 毅. いまさら聞けない薬物動態Q&A: 薬剤師が知っておきたい抱合酵素とその基質について教えてください. 月刊薬事, 2016; 58: 685-690.
- 2015年
- Iwamura A, Ito M, Mitsui H, Hasegawa J, Kosaka K, Kino I, Tsuda M, Nakajima M, Yokoi T, Kume T. Toxicological evaluation of acyl glucuronides utilizing half-lives, peptide adducts, and immunostimulation assays. Toxicol In Vitro, 2015; 30: 241-249.
- Nakajima A, Aoyama Y, Shin EJ, Nam Y, Kim HC, Nagai T, Yokosuka A, Mimaki Y, Yokoi T, Ohizumi Y, Yamada K. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, improves cognitive impairment and reduces soluble Abeta levels in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (3XTg-AD). Behav Brain Res, 2015; 289: 69-77.
- Tomida T, Okamura H, Satsukawa M, Yokoi T, Konno Y. Multiparametric assay using HepaRG cells for predicting drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett, 2015; 236: 16-24.
- Iida A, Sasaki E, Yano A, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Carbamazepine-induced liver injury requires CYP3A-mediated metabolism and glutathione depletion in rats. Drug Metab Dispos, 2015; 43: 958-968.
- Oda S, Fujiwara R, Kutsuno Y, Fukami T, Itoh T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Targeted screen for human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases inhibitors and the evaluation of potential drug-drug interactions with zafirlukast. Drug Metab Dispos, 2015; 43: 812-818.
- Nakano M, Fukushima Y, Yokota S, Fukami T, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. CYP2A7 pseudogene transcript affects CYP2A6 expression in human liver by acting as a decoy for miR-126. Drug Metab Dispos, 2015; 43: 703-712.
- Lim YP, Cheng CH, Chen WC, Chang SY, Hung DZ, Chen JJ, Wan L, Ma WC, Lin YH, Chen CY, Yokoi T, Nakajima M, Chen CJ. Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) inhibits pregnane X receptor (PXR) and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) activation and protects against acetaminophen- and amiodarone-induced cytotoxicity. Arch Toxicol, 2015; 89: 57-72.
- Takai S, Higuchi S, Yano A, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Involvement of immune- and inflammatory-related factors in flucloxacillin-induced liver injury in mice. J Appl Toxicol, 2015; 35: 142-151.
- Oda S, Yokoi T. Establishment of animal models of drug-induced liver injury and analysis of possible mechanisms. Yakugaku Zasshi, 2015; 135: 579-588.
- Oda S, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. A comprehensive review of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase and esterases for drug development. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2015; 30: 30-51.
- 2014年
- Ito Y, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. An orphan esterase ABHD10 modulates probenecid acyl glucuronidation in human liver. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014; 42: 2109-2116.
- Sasaki E, Iwamura A, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Kume T, Yokoi T. Role of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism and identification of novel thiol-conjugated metabolites in mice with phenytoin-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett, 2014; 232: 79-88.
- Lim YP, Chen WC, Cheng CH, Ma WC, Lin YH, Chen CY, Hung DZ, Chen JJ, Yokoi T, Nakajima M, Chen CJ. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 2C9 expression and activity in vitro by allyl isothiocyanate. Planta Med, 2014; 80: 1097-1106.
- Kurth MJ, Yokoi T, Gershwin ME. Halothane-induced hepatitis: paradigm or paradox for drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology, 2014; 60: 1473-1475.
- Yamaura Y, Nakajima M, Tatsumi N, Takagi S, Fukami T, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. Changes in the expression of miRNAs at the pericentral and periportal regions of the rat liver in response to hepatocellular injury: comparison with the changes in the expression of plasma miRNAs. Toxicology, 2014; 322: 89-98.
- Oda Y, Nakajima M, Tsuneyama K, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Fukami T, Yokoi T. Retinoid X receptor alpha in human liver is regulated by miR-34a. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014; 90: 179-187.
- Shimizu M, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Screening of specific inhibitors for human carboxylesterases or arylacetamide deacetylase. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014; 42: 1103-1109.
- Yano A, Oda S, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Development of a cell-based assay system considering drug metabolism and immune- and inflammatory-related factors for the risk assessment of drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett, 2014; 228: 13-24.
- Tang SC, Sparidans RW, Cheung KL, Fukami T, Durmus S, Wagenaar E, Yokoi T, van Vlijmen BJ, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH. P-glycoprotein, CYP3A, and plasma carboxylesterase determine brain and blood disposition of the mTOR Inhibitor everolimus (Afinitor) in mice. Clin Cancer Res, 2014; 20: 3133-3145.
- Endo S, Yano A, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Involvement of miRNAs in the early phase of halothane-induced liver injury. Toxicology, 2014; 319: 75-84.
- Takahashi K, Tatsumi N, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Integrated analysis of rifampicin-induced microRNA and gene expression changes in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2014; 29: 333-340.
- Shimizu M, Fukami T, Ito Y, Kurokawa T, Kariya M, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Indiplon is hydrolyzed by arylacetamide deacetylase in human liver. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014; 42: 751-758.
- Oda S, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Epigenetic regulation of the tissue-specific expression of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A10. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014; 87: 660-667.
- Kuno S, Sakurai F, Shimizu K, Matsumura N, Kim S, Watanabe H, Tashiro K, Tachibana M, Yokoi T, Mizuguchi H. Development of mice exhibiting hepatic microsomal activity of human CYP3A4 comparable to that in human liver microsomes by intravenous administration of an adenovirus vector expressing human CYP3A4. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2014; 29: 296-304.
- Matsuo K, Sasaki E, Higuchi S, Takai S, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Involvement of oxidative stress and immune- and inflammation-related factors in azathioprine-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett, 2014; 224: 215-224.
- Muta K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. N-Glycosylation during translation is essential for human arylacetamide deacetylase enzyme activity. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014; 87: 352-359.
- Miyashita T, Kimura K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Evaluation and mechanistic analysis of the cytotoxicity of the acyl glucuronide of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014; 42: 1-8.
- Takahashi K, Oda Y, Toyoda Y, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Regulation of cytochrome b5 expression by miR-223 in human liver: effects on cytochrome P450 activities. Pharm Res, 2014; 31: 780-794.
- 織田進吾, 横井 毅. 薬物性肝障害における免疫・炎症因子の関与. 日本皮膚アレルギー・接触皮膚炎学会雑誌, 2014; 8: 239-248.
- 横井 毅.肝障害とバイオマーカーとしてのmiRNA. 谷本学校 毒性質問箱, 2014; 16:56-67.
- Yokoi T. New prospectives and understanding in drug-induced liver injury considering drug metabolism and immune- and inflammation-related factors. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi, 2014; 144: 22-27.
- 横井 毅.薬物代謝と肝障害. 月刊薬事, 2014 56: 21-25.
- Miki Nakajima and Tsuyoshi Yokoi. MicroRNA-regulation of P450 and pharmacogenetics. Sandosh Padmanabhan Ed. Handbook Pharmacogenomics and Stratified Medicines, Elsevier, Watham, pp.385-401, 2014.
- 2013年
- Sasaki E, Matsuo K, Iida A, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. A novel mouse model for phenytoin-induced liver injury: involvement of immune-related factors and P450-mediated metabolism. Toxicol Sci, 2013; 136: 250-263.
- Takahashi K, Yokota S, Tatsumi N, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Cigarette smoking substantially alters plasma microRNA profiles in healthy subjects. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2013; 272: 154-160.
- Kato Y, Izukawa T, Oda S, Fukami T, Finel M, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 2B10 in drug N-glucuronidation: substrate screening and comparison with UGT1A3 and UGT1A4. Drug Metab Dispos, 2013; 41: 1389-1397.
- Higuchi R, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Prilocaine- and lidocaine-induced methemoglobinemia is caused by human carboxylesterase-, CYP2E1-, and CYP3A4-mediated metabolic activation. Drug Metab Dispos, 2013; 41: 1220-1230.
- Oda S, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Epigenetic regulation is a crucial factor in the repression of UGT1A1 expression in the human kidney. Drug Metab Dispos, 2013; 41: 1738-1743.
- Poon CH, Wong TY, Wang Y, Tsuchiya Y, Nakajima M, Yokoi T, Leung LK. The citrus flavanone naringenin suppresses CYP1B1 transactivation through antagonising xenobiotic-responsive element binding. Br J Nutr, 2013; 109: 1598-1605.
- Kataoka M, Terashima Y, Mizuno K, Masaoka Y, Sakuma S, Yokoi T, Yamashita S. Establishment of MDCKII cell monolayer with metabolic activity by CYP3A4 transduced with recombinant adenovirus. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2013; 28: 125-131.
- Yokoi T. A new era in the study of individual differences in drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2013; 28: 1-2.
- Yokoi T, Nakajima M. microRNAs as mediators of drug toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 2013; 53: 377-400.
- 横井 毅.体内動態と薬物相互作用の基礎と応用-食品成分への展開-.食品加工技術, 2013; 33: 7-13.
- 横井 毅. 薬物代謝反応・代謝酵素の多様性と薬物相互作用の予測 p198-204. 「In vitro毒性・動態評価の最前線」小島肇監修、シーエムシー出, 2013.
- 2012年
- Kobayashi Y, Fukami T, Higuchi R, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Metabolic activation by human arylacetamide deacetylase, CYP2E1, and CYP1A2 causes phenacetin-induced methemoglobinemia. Biochem Pharmacol, 2012; 84: 1196-1206.
- Kakuni M, Morita M, Matsuo K, Katoh Y, Nakajima M, Tateno C, Yokoi T. Chimeric mice with a humanized liver as an animal model of troglitazone-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett, 2012; 214: 9-18.
- Higuchi S, Yano A, Takai S, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Metabolic activation and inflammation reactions involved in carbamazepine-induced liver injury. Toxicol Sci, 2012; 130: 4-16.
- Miyashita T, Toyoda Y, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Hepatoprotective effect of tamoxifen on steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mouse models. J Toxicol Sci, 2012; 37: 931-942.
- Yoshikawa Y, Miyashita T, Higuchi S, Tsuneyama K, Endo S, Tsukui T, Toyoda Y, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Mechanisms of the hepatoprotective effects of tamoxifen against drug-induced and chemical-induced acute liver injuries. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2012; 264: 42-50.
- Oda S, Nakajima M, Hatakeyama M, Fukami T, Yokoi T. Preparation of a specific monoclonal antibody against human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A9 and evaluation of UGT1A9 protein levels in human tissues. Drug Metab Dispos, 2012; 40: 1620-1627.
- Endo S, Toyoda Y, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Stimulation of human monocytic THP-1 cells by metabolic activation of hepatotoxic drugs. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2012; 27: 621-630.
- Kobayashi Y, Fukami T, Shimizu M, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Contributions of arylacetamide deacetylase and carboxylesterase 2 to flutamide hydrolysis in human liver. Drug Metab Dispos, 2012; 40: 1080-1084.
- Shimizu M, Fukami T, Kobayashi Y, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. A novel polymorphic allele of human arylacetamide deacetylase leads to decreased enzyme activity. Drug Metab Dispos, 2012; 40: 1183-1190.
- Kulthong K, Maniratanachote R, Kobayashi Y, Fukami T, Yokoi T. Effects of silver nanoparticles on rat hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme activity. Xenobiotica, 2012; 42: 854-862.
- Oda Y, Nakajima M, Mohri T, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Fukami T, Yokoi T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator in human liver is regulated by miR-24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2012; 260: 222-231.
- Iwamura A, Fukami T, Higuchi R, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Human alpha/beta hydrolase domain containing 10 (ABHD10) is responsible enzyme for deglucuronidation of mycophenolic acid acyl-glucuronide in liver. J Biol Chem, 2012; 287: 9240-9249.
- Yano A, Higuchi S, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Involvement of immune-related factors in diclofenac-induced acute liver injury in mice. Toxicology, 2012; 293: 107-114.
- Taesotikul T, Nakajima M, Tassaneeyakul W, Yokoi T. Effects of Phyllanthus amarus on the pharmacokinetics of midazolam and cytochrome P450 activities in rats. Xenobiotica, 2012; 42: 641-648.
- Kobayashi M, Higuchi S, Ide M, Nishikawa S, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Th2 cytokine-mediated methimazole-induced acute liver injury in mice. J Appl Toxicol, 2012; 32: 823-833.
- Kobayashi Y, Fukami T, Nakajima A, Watanabe A, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Species differences in tissue distribution and enzyme activities of arylacetamide deacetylase in human, rat, and mouse. Drug Metab Dispos, 2012; 40: 671-679.
- Yamaura Y, Nakajima M, Takagi S, Fukami T, Tsuneyama K, Yokoi T. Plasma microRNA profiles in rat models of hepatocellular injury, cholestasis, and steatosis. PLoS One, 2012; 7: e30250.
- Toyoda Y, Endo S, Tsuneyama K, Miyashita T, Yano A, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Mechanism of exacerbative effect of progesterone on drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Sci, 2012; 126: 16-27.
- Kato Y, Nakajima M, Oda S, Fukami T, Yokoi T. Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms involved in haloperidol glucuronidation and quantitative estimation of their contribution. Drug Metab Dispos, 2012; 40: 240-248.
- Higuchi S, Kobayashi M, Yano A, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Involvement of Th2 cytokines in the mouse model of flutamide-induced acute liver injury. J Appl Toxicol, 2012; 32: 815-822.
- Fukami T, Yokoi T. The emerging role of human esterases. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2012; 27: 466-477.
- 2011年
- Oda S, Nakajima M, Toyoda Y, Fukami T, Yokoi T. Progesterone receptor membrane component 1 modulates human cytochrome p450 activities in an isoform-dependent manner. Drug Metab Dispos, 2011; 39: 2057-2065.
- Nakajima A, Fukami T, Kobayashi Y, Watanabe A, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Human arylacetamide deacetylase is responsible for deacetylation of rifamycins: rifampicin, rifabutin, and rifapentine. Biochem Pharmacol, 2011; 82: 1747-1756.
- Kida K, Nakajima M, Mohri T, Oda Y, Takagi S, Fukami T, Yokoi T. PPARalpha is regulated by miR-21 and miR-27b in human liver. Pharm Res, 2011; 28: 2467-2476.
- Hosomi H, Fukami T, Iwamura A, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Development of a highly sensitive cytotoxicity assay system for CYP3A4-mediated metabolic activation. Drug Metab Dispos, 2011; 39: 1388-1395.
- Hioki T, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Human paraoxonase 1 is the enzyme responsible for pilocarpine hydrolysis. Drug Metab Dispos, 2011; 39: 1345-1352.
- Usui T, Hashizume T, Katsumata T, Yokoi T, Komuro S. In vitro investigation of the glutathione transferase M1 and T1 null genotypes as risk factors for troglitazone-induced liver injury. Drug Metab Dispos, 2011; 39: 1303-1310.
- Toyoda Y, Miyashita T, Endo S, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Estradiol and progesterone modulate halothane-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicol Lett, 2011; 204: 17-24.
- Iwamura A, Fukami T, Hosomi H, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. CYP2C9-mediated metabolic activation of losartan detected by a highly sensitive cell-based screening assay. Drug Metab Dispos, 2011; 39: 838-846.
- Abe Y, Fujiwara R, Oda S, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Interpretation of the effects of protein kinase C inhibitors on human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A (UGT1A) proteins in cellulo. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2011; 26: 256-265.
- Higuchi S, Kobayashi M, Yoshikawa Y, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. IL-4 mediates dicloxacillin-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicol Lett, 2011; 200: 139-145.
- Koga T, Fujiwara R, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Toxicological evaluation of acyl glucuronides of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs using human embryonic kidney 293 cells stably expressing human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase and human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos, 2011; 39: 54-60.
- Yokota S, Higashi E, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Human CYP2A6 is regulated by nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2. Biochem Pharmacol, 2011; 81: 289-294.
- Mizuno K, Toyoda Y, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Stimulation of pro-inflammatory responses by mebendazole in human monocytic THP-1 cells through an ERK signaling pathway. Arch Toxicol, 2011; 85: 199-207.
- Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Toxicological implications of modulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Toxicol Sci, 2011; 123: 1-14.
- Yokoi T. Current topics in drug metabolism and drug toxicity. Preface. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2011; 26: 1-2.
- Nakajima M, Yokoi T. MicroRNAs from biology to future pharmacotherapy: regulation of cytochrome P450s and nuclear receptors. Pharmacol Ther, 2011; 131: 330-337.
- 横井 毅. 第II相代謝の評価と創薬 p224-231.「医薬品開発に必要なストラテジーと各種試験法」日本薬理学会編, 2011.
- 2010年
- Watanabe A, Fukami T, Takahashi S, Kobayashi Y, Nakagawa N, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Arylacetamide deacetylase is a determinant enzyme for the difference in hydrolase activities of phenacetin and acetaminophen. Drug Metab Dispos, 2010; 38: 1532-1537.
- Kobayashi M, Higuchi S, Mizuno K, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Interleukin-17 is involved in alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicology, 2010; 275: 50-57.
- Fukami T, Nakajima M, Matsumoto I, Zen Y, Oda M, Yokoi T. Immunohistochemical analysis of CYP2A13 in various types of human lung cancers. Cancer Sci, 2010; 101: 1024-1028.
- Fukami T, Takahashi S, Nakagawa N, Maruichi T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. In vitro evaluation of inhibitory effects of antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic drugs on human carboxylesterase activities. Drug Metab Dispos, 2010; 38: 2173-2178.
- Mizuno K, Fukami T, Toyoda Y, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Terbinafine stimulates the pro-inflammatory responses in human monocytic THP-1 cells through an ERK signaling pathway. Life Sci, 2010; 87: 537-544.
- Holmes RS, Wright MW, Laulederkind SJ, Cox LA, Hosokawa M, Imai T, Ishibashi S, Lehner R, Miyazaki M, Perkins EJ, Potter PM, Redinbo MR, Robert J, Satoh T, Yamashita T, Yan B, Yokoi T, Zechner R, Maltais LJ. Recommended nomenclature for five mammalian carboxylesterase gene families: human, mouse, and rat genes and proteins. Mamm Genome, 2010; 21: 427-441.
- Takagi S, Nakajima M, Kida K, Yamaura Y, Fukami T, Yokoi T. MicroRNAs regulate human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha, modulating the expression of metabolic enzymes and cell cycle. J Biol Chem, 2010; 285: 4415-4422.
- Hosomi H, Akai S, Minami K, Yoshikawa Y, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. An in vitro drug-induced hepatotoxicity screening system using CYP3A4-expressing and gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase knockdown cells. Toxicol In Vitro, 2010; 24: 1032-1038.
- Nakajima M, Koga T, Sakai H, Yamanaka H, Fujiwara R, Yokoi T. N-Glycosylation plays a role in protein folding of human UGT1A9. Biochem Pharmacol, 2010; 79: 1165-1172.
- Mohri T, Nakajima M, Fukami T, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Yokoi T. Human CYP2E1 is regulated by miR-378. Biochem Pharmacol, 2010; 79: 1045-1052.
- Maruichi T, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Transcriptional regulation of human carboxylesterase 1A1 by nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2). Biochem Pharmacol, 2010; 79: 288-295.
- Fujiwara R, Nakajima M, Oda S, Yamanaka H, Ikushiro S, Sakaki T, Yokoi T. Interactions between human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 2B7 and UGT1A enzymes. J Pharm Sci, 2010; 99: 442-454.
- 横井 毅. 薬物動態関連遺伝子の多型と薬物相互作用. 臨床検査, 2010; 54: 1107-1113.
- 横井 毅. 薬物代謝異常と小胞体 p235-250. 「生物薬科学実験講座5、細胞の構造とオルガネラ」大熊勝治、中西義信編集、廣川書店, 2010.
- 横井 毅. 薬物代謝に関与する酵素とその反応機構 p43-68、 薬物代謝と毒性発現 p182-192.「薬物代謝学 医療薬学・医薬品開発の基礎として第3版」加藤隆一、山添 康、横井 毅編、 東京化学同人, 2010.
- Tsuyoshi Yokoi. Troglitazone p419-435. 「Adverse Drug Reactions」 Jack Uetrecht Ed. in Handbook of Expreimental Pharmacology 196, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2010.
- 2009年
- Nakagawa N, Katoh M, Yoshioka Y, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Inhibitory effects of Kampo medicine on human UGT2B7 activity. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2009; 24: 490-499.
- Yoshikawa Y, Morita M, Hosomi H, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Knockdown of superoxide dismutase 2 enhances acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Toxicology, 2009; 264: 89-95.
- Kobayashi E, Kobayashi M, Tsuneyama K, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Halothane-induced liver injury is mediated by interleukin-17 in mice. Toxicol Sci, 2009; 111: 302-310.
- Komagata S, Nakajima M, Takagi S, Mohri T, Taniya T, Yokoi T. Human CYP24 catalyzing the inactivation of calcitriol is post-transcriptionally regulated by miR-125b. Mol Pharmacol, 2009; 76: 702-709.
- Yoshikawa Y, Hosomi H, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Establishment of knockdown of superoxide dismutase 2 and expression of CYP3A4 cell system to evaluate drug-induced cytotoxicity. Toxicol In Vitro, 2009; 23: 1179-1187.
- Morita M, Akai S, Hosomi H, Tsuneyama K, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity test using gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase knockdown rat. Toxicol Lett, 2009; 189: 159-165.
- Izukawa T, Nakajima M, Fujiwara R, Yamanaka H, Fukami T, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Ikushiro S, Sakaki T, Yokoi T. Quantitative analysis of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A and UGT2B expression levels in human livers. Drug Metab Dispos, 2009; 37: 1759-1768.
- Watanabe A, Fukami T, Nakajima M, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Yokoi T. Human arylacetamide deacetylase is a principal enzyme in flutamide hydrolysis. Drug Metab Dispos, 2009; 37: 1513-1520.
- Mohri T, Nakajima M, Takagi S, Komagata S, Yokoi T. MicroRNA regulates human vitamin D receptor. Int J Cancer, 2009; 125: 1328-1333.
- Volotinen M, Maenpaa J, Kankuri E, Oksala O, Pelkonen O, Nakajima M, Yokoi T, Hakkola J. Expression of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes in human nonpigmented ciliary epithelial cells: induction of CYP1B1 expression by TCDD. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2009; 50: 3099-3105.
- Takahashi S, Katoh M, Saitoh T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Different inhibitory effects in rat and human carboxylesterases. Drug Metab Dispos, 2009; 37: 956-961.
- Ishihara K, Katsutani N, Asai N, Inomata A, Uemura Y, Suganuma A, Sawada K, Yokoi T, Aoki T. Identification of urinary biomarkers useful for distinguishing a difference in mechanism of toxicity in rat model of cholestasis. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 2009; 105: 156-166.
- Fujiwara R, Nakajima M, Yamamoto T, Nagao H, Yokoi T. In silico and in vitro approaches to elucidate the thermal stability of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A9. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2009; 24: 235-244.
- Katoh M, Yoshioka Y, Nakagawa N, Yokoi T. Effects of Japanese herbal medicine, Kampo, on human UGT1A1 activity. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2009; 24: 226-234.
- Mizuno K, Katoh M, Okumura H, Nakagawa N, Negishi T, Hashizume T, Nakajima M, Yokoi T. Metabolic activation of benzodiazepines by CYP3A4. Drug Metab Dispos, 2009; 37: 345-351.
- Fujiwara R, Nakajima M, Yamanaka H, Yokoi T. Key amino acid residues responsible for the differences in substrate specificity of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A9 and UGT1A8. Drug Metab Dispos, 2009; 37: 41-46.
- Yokoi T. Essentials for starting a pediatric clinical study (1): Pharmacokinetics in children. J Toxicol Sci, 2009; 34 Suppl 2: SP307-312.
- 横井 毅. 薬物動態と医薬品の薬効・副作用:代謝を中心として.治療学, 2009; 43: 1262-1266.
- 横井 毅. 第II相代謝の評価と創薬:化合物から医薬品にするために必要な薬物動態試験. 日本薬理学雑誌, 2009; 134: 334-337.
- 横井 毅. 薬物動態関連遺伝子の多型と薬物相互作用.DNA多型, 2009; 17: 6-10.
- 横井 毅. 薬物の作用, 薬物動態の基本 p9-20.「医薬品トキシコロジー 改訂第4版」佐藤哲男、仮家公夫、北田光一編、南江堂, 2009.
- 横井 毅. 薬物療法の個人差と薬物代謝酵素の遺伝子多型 p43-47. ひらかれた小児リウマチ治療、セカンド出版, 2009.
- 横井 毅.毒科学とゲノムサイエンス・トキシコゲノミクス p56-60「標準医療薬学 薬理学」辻本豪三、小池勝夫編、医学書院, 2009.
| 専攻 | 総合医学専攻 |
|---|---|
| 大講座 | 分子医薬学 |
| 分野 | トキシコゲノミクス |